
前端(vue)入門到精通課程,老師在線輔導:聯系老師
Apipost = Postman + Swagger + Mock + Jmeter 超好用的API調試工具:點擊使用
路由的概念相信大部分同學并不陌生,我們在用 Vue 開發過實際項目的時候都會用到 Vue-Router 這個官方插件來幫我們解決路由的問題。它的作用就是根據不同的路徑映射到不同的視圖。本文不再講述路由的基礎使用和API,不清楚的同學可以自行查閱官方文檔vue-router3 對應 vue2 和 vue-router4 對應 vue3。
今天我們主要是談談Vue-Router的實現原理,感興趣的小伙伴可以繼續往下看,大佬請止步。
本文 vue-router 版本為 3.5.3
路由
既然我們在分析路由,我們首先來說說什么是路由,什么是后端路由、什么是前端路由。
路由就是根據不同的 url 地址展示不同的內容或頁面,早期路由的概念是在后端出現的,通過服務器端渲染后返回頁面,隨著頁面越來越復雜,服務器端壓力越來越大。后來ajax異步刷新的出現使得前端也可以對url進行管理,此時,前端路由就出現了。(學習視頻分享:web前端開發、編程基礎視頻)
我們先來說說后端路由
后端路由
后端路由又可稱之為服務器端路由,因為對于服務器來說,當接收到客戶端發來的HTTP請求,就會根據所請求的URL,來找到相應的映射函數,然后執行該函數,并將函數的返回值發送給客戶端。
對于最簡單的靜態資源服務器,可以認為,所有URL的映射函數就是一個文件讀取操作。 對于動態資源,映射函數可能是一個數據庫讀取操作,也可能是進行一些數據的處理,等等。
然后根據這些讀取的數據,在服務器端就使用相應的模板來對頁面進行渲染后,再返回渲染完畢的HTML頁面。早期的jsp就是這種模式。
前端路由
剛剛也介紹了,在前后端沒有分離的時候,服務端都是直接將整個 HTML 返回,用戶每次一個很小的操作都會引起頁面的整個刷新(再加上之前的網速還很慢,所以用戶體驗可想而知)。
在90年代末的時候,微軟首先實現了 ajax(Asynchronous JavaScript And XML) 這個技術,這樣用戶每次的操作就可以不用刷新整個頁面了,用戶體驗就大大提升了。
雖然數據能異步獲取不用每個點擊都去請求整個網頁,但是頁面之間的跳轉還是會加載整個網頁,體驗不是特別好,還有沒有更好的方法呢?
至此異步交互體驗的更高級版本 SPA單頁應用 就出現了。單頁應用不僅僅是在頁面交互是無刷新的,連頁面跳轉都是無刷新的。既然頁面的跳轉是無刷新的,也就是不再向后端請求返回 HTML頁面。
頁面跳轉都不從后端獲取新的HTML頁面,那應該怎么做呢?所以就有了現在的前端路由。
可以理解為,前端路由就是將之前服務端根據 url 的不同返回不同的頁面的任務交給前端來做。在這個過程中,js會實時檢測url的變化,從而改變顯示的內容。
前端路由優點是用戶體驗好,用戶操作或頁面跳轉不會刷新頁面,并且能快速展現給用戶。缺點是首屏加載慢,因為需要js動態渲染展示內容。而且由于內容是js動態渲染的所以不利于SEO。
下面我們正式進入Vue-Router原理分析階段。
分析Vue-Router.install方法
我們先來看看install.js,這個方法會在Vue.use(VueRouter)的時候被調用。
// install.js import View from './components/view' import Link from './components/link' export let _Vue export function install (Vue) { // 不會重復安裝 if (install.installed && _Vue === Vue) return install.installed = true _Vue = Vue const isDef = v => v !== undefined // 為router-view組件關聯路由組件 const registerInstance = (vm, callVal) => { let i = vm.$options._parentVnode // 調用vm.$options._parentVnode.data.registerRouteInstance方法 // 而這個方法只在router-view組件中存在,router-view組件定義在(../components/view.js @71行) // 所以,如果vm的父節點為router-view,則為router-view關聯當前vm,即將當前vm做為router-view的路由組件 if (isDef(i) && isDef(i = i.data) && isDef(i = i.registerRouteInstance)) { i(vm, callVal) } } Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate () { // 這里只會進來一次,因為只有Vue根實例才會有router屬性。 if (isDef(this.$options.router)) { // 所以這里的this就是Vue根實例 this._routerRoot = this this._router = this.$options.router this._router.init(this) // 將 _route 變成響應式 Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current) } else { // 子組件會進入這里,這里也是把Vue根實例保存帶_routerRoot屬性上 this._routerRoot = (this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot) || this } // 為router-view組件關聯路由組件 registerInstance(this, this) }, destroyed () { // destroyed hook觸發時,取消router-view和路由組件的關聯 registerInstance(this) } }) // 在原型上注入$router、$route屬性,方便快捷訪問 Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$router', { // 上面說到每個組件的_routerRoot都是Vue根實例,所以都能訪問_router get () { return this._routerRoot._router } }) // 每個組件訪問到的$route,其實最后訪問的都是Vue根實例的_route Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$route', { get () { return this._routerRoot._route } }) // 注冊router-view、router-link兩個全局組件 Vue.component('RouterView', View) Vue.component('RouterLink', Link) const strats = Vue.config.optionMergeStrategies // use the same hook merging strategy for route hooks strats.beforeRouteEnter = strats.beforeRouteLeave = strats.beforeRouteUpdate = strats.created }
主要做了如下幾件事情:
避免重復安裝
為了確保 install 邏輯只執行一次,用了 install.installed 變量做已安裝的標志位。
傳遞Vue引用減少打包體積
用一個全局的 _Vue 來接收參數 Vue,因為作為 Vue 的插件對 Vue 對象是有依賴的,但又不能去單獨去 import Vue,因為那樣會增加包體積,所以就通過這種方式拿到 Vue 對象。
注冊全局混入
Vue-Router 安裝最重要的一步就是利用 Vue.mixin,在beforeCreate和destroyed生命周期函數中注入路由邏輯。
Vue.mixin我們知道就是全局 mixin,所以也就相當于每個組件的beforeCreate和destroyed生命周期函數中都會有這些代碼,并在每個組件中都會運行。
Vue.mixin({ beforeCreate () { if (isDef(this.$options.router)) { this._routerRoot = this this._router = this.$options.router this._router.init(this) Vue.util.defineReactive(this, '_route', this._router.history.current) } else { this._routerRoot = (this.$parent && this.$parent._routerRoot) || this } registerInstance(this, this) }, destroyed () { registerInstance(this) } })
在這兩個鉤子中,this是指向當時正在調用鉤子的vue實例。
這兩個鉤子中的邏輯,在安裝流程中是不會被執行的,只有在組件實例化時執行到鉤子時才會被調用
先看混入的 beforeCreate 鉤子函數
它先判斷了this.$options.router是否存在,我們在new Vue({router})時,router才會被保存到到Vue根實例的$options上,而其它Vue實例的$options上是沒有router的,所以if中的語句只在this === new Vue({router})時,才會被執行,由于Vue根實例只有一個,所以這個邏輯只會被執行一次。
對于根 Vue 實例而言,執行該鉤子函數時定義了 this._routerRoot 表示它自身(Vue根實例);this._router 表示 VueRouter 的實例 router,它是在 new Vue 的時候傳入的;
另外執行了 this._router.init() 方法初始化 router,這個邏輯在后面講初始化的時候再介紹。
然后用 defineReactive 方法把 this._route 變成響應式對象,保證_route變化時,router-view會重新渲染,這個我們后面在router-view組件中會細講。
我們再看下else中具體干了啥
主要是為每個組件定義_routerRoot,對于子組件而言,由于組件是樹狀結構,在遍歷組件樹的過程中,它們在執行該鉤子函數的時候 this._routerRoot 始終指向的離它最近的傳入了 router 對象作為配置而實例化的父實例(也就是永遠等于根實例)。
所以我們可以得到,在每個vue組件都有 this._routerRoot === vue根實例、this._routerRoot._router === router對象
對于 beforeCreate 和 destroyed 鉤子函數,它們都會執行 registerInstance 方法,這個方法的作用我們也是之后會介紹。
添加$route、$router屬性
接著給 Vue 原型上定義了 $router 和 $route 2 個屬性的 get 方法,這就是為什么我們可以在任何組件實例上都可以訪問 this.$router 以及 this.$route。
Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$router', { get () { return this._routerRoot._router } }) Object.defineProperty(Vue.prototype, '$route', { get () { return this._routerRoot._route } })
我們可以看到,$router其實返回的是this._routerRoot._router,也就是vue根實例上的router,因此我們可以通過this.$router來使用router的各種方法。
$route其實返回的是this._routerRoot._route,其實就是this._router.history.current,也就是目前的路由對象,這個后面會細說。
注冊全局組件
通過 Vue.component 方法定義了全局的 <router-link> 和 <router-view> 2 個組件,這也是為什么我們在寫模板的時候可以直接使用這兩個標簽,它們的作用我想就不用筆者再說了吧。
鉤子函數的合并策略
最后設置路由組件的beforeRouteEnter、beforeRouteLeave、beforeRouteUpdate守衛的合并策略。
總結
那么到此為止,我們分析了 Vue-Router 的安裝過程,Vue 編寫插件的時候通常要提供靜態的 install 方法,我們通過 Vue.use(plugin) 時候,就是在執行 install 方法。Vue-Router 的 install 方法會給每一個組件注入 beforeCreate 和 destoryed 鉤子函數,在beforeCreate 做一些私有屬性定義和路由初始化工作。并注冊了兩個全局組件,然后設置了鉤子函數合并策略。在destoryed 做了一些銷毀工作。
下面我們再來看看Vue-Router的實例化。
分析init方法
前面我們提到了在 install 的時候會執行 VueRouter 的 init 方法( this._router.init(this) ),那么接下來我們就來看一下 init 方法做了什么。
init (app: any /* Vue component instance */) { // ... this.apps.push(app) // ... // main app previously initialized // return as we don't need to set up new history listener if (this.app) { return } this.app = app const history = this.history if (history instanceof HTML5History || history instanceof HashHistory) { const handleInitialScroll = routeOrError => { const from = history.current const expectScroll = this.options.scrollBehavior const supportsScroll = supportsPushState && expectScroll if (supportsScroll && 'fullPath' in routeOrError) { handleScroll(this, routeOrError, from, false) } } // 1.setupListeners 里會對 hashchange或popstate事件進行監聽 const setupListeners = routeOrError => { history.setupListeners() handleInitialScroll(routeOrError) } // 2.初始化導航 history.transitionTo( history.getCurrentLocation(), setupListeners, setupListeners ) } // 3.路由全局監聽,維護當前的route // 當路由變化的時候修改app._route的值 // 由于_route是響應式的,所以修改后相應視圖會同步更新 history.listen(route => { this.apps.forEach(app => { app._route = route }) }) }
這里主要做了如下幾件事情:
設置了路由監聽
const setupListeners = routeOrError => { history.setupListeners() handleInitialScroll(routeOrError) }
這里會根據當前路由模式監聽hashchange或popstate事件,當事件觸發的時候,會進行路由的跳轉。(后面說到路由模式的時候會細說)
初始化導航
history.transitionTo( history.getCurrentLocation(), setupListeners, setupListeners )
進入系統會進行初始化路由匹配,渲染對應的組件。因為第一次進入系統,并不會觸發hashchange或者popstate事件,所以第一次需要自己手動匹配路徑然后進行跳轉。
路由全局監聽
history.listen(route => { this.apps.forEach(app => { app._route = route }) })
當路由變化的時候修改app._route的值。由于_route是響應式的,所以修改后相應視圖會同步更新。
總結
這里主要是做了一些初始化工作。根據當前路由模式監聽對應的路由事件。初始化導航,根據當前的url渲染初始頁面。最后切換路由的時候修改_route,由于_route是響應式的,所以修改后相應視圖會同步更新。
分析VueRouter實例化
實例化就是我們new VueRouter({routes})的過程,我們來重點分析下VueRouter的構造函數。
constructor (options: RouterOptions = {}) { // ... // 參數初始化 this.app = null this.apps = [] this.options = options this.beforeHooks = [] this.resolveHooks = [] this.afterHooks = [] // 創建matcher this.matcher = createMatcher(options.routes || [], this) // 設置默認模式和做不支持 H5 history 的降級處理 let mode = options.mode || 'hash' this.fallback = mode === 'history' && !supportsPushState && options.fallback !== false if (this.fallback) { mode = 'hash' } if (!inBrowser) { mode = 'abstract' } this.mode = mode // 根據不同的 mode 實例化不同的 History 對象 switch (mode) { case 'history': this.history = new HTML5History(this, options.base) break case 'hash': this.history = new HashHistory(this, options.base, this.fallback) break case 'abstract': this.history = new AbstractHistory(this, options.base) break default: if (process.env.NODE_ENV !== 'production') { assert(false, `invalid mode: ${mode}`) } } }
這里主要做了如下幾件事情:
初始化參數
我們看到在最開始有些參數的初始化,這些參數到底是什么呢?
this.app 用來保存根 Vue 實例。
this.apps 用來保存持有 $options.router 屬性的 Vue 實例。
this.options 保存傳入的路由配置,也就是前面說的RouterOptions。
this.beforeHooks、 this.resolveHooks、this.afterHooks 表示一些鉤子函數。
this.fallback 表示在瀏覽器不支持 history 新api的情況下,根據傳入的 fallback 配置參數,決定是否回退到hash模式。
this.mode 表示路由創建的模式。
創建matcher
matcher,匹配器。簡單理解就是可以通過url找到我們對應的組件。這一塊內容較多,這里筆者就不再詳細分析了。
確定路由模式
路由模式平時都會只說兩種,其實在vue-router總共實現了 hash、history、abstract 3 種模式。
VueRouter會根據options.mode、options.fallback、supportsPushState、inBrowser來確定最終的路由模式。
如果沒有設置mode就默認是hash模式。
確定fallback值,只有在用戶設置了mode:history并且當前環境不支持pushState且用戶沒有主動聲明不需要回退(沒設置fallback值位undefined),此時this.fallback才為true,當fallback為true時會使用hash模式。(簡單理解就是如果不支持history模式并且只要沒設置fallback為false,就會啟用hash模式)
如果最后發現處于非瀏覽器環境,則會強制使用abstract模式。
實例化路由模式
根據mode屬性值來實例化不同的對象。VueRouter的三種路由模式,主要由下面的四個核心類實現
-
History- 基礎類
- 位于
src/history/base.js
-
HTML5History- 用于支持
pushState的瀏覽器 src/history/html5.js
- 用于支持
-
HashHistory- 用于不支持
pushState的瀏覽器 src/history/hash.js
- 用于不支持
-
AbstractHistory- 用于非瀏覽器環境(服務端渲染)
src/history/abstract.js
HTML5History、HashHistory、AbstractHistory三者都是繼承于基礎類History。
這里我們詳細分析下HTML5History和HashHistory類。
HTML5History類
當我們使用history模式的時候會實例化HTML5History類
// src/history/html5.js ... export class HTML5History extends History { _startLocation: string constructor (router: Router, base: ?string) { // 調用父類構造函數初始化 super(router, base) this._startLocation = getLocation(this.base) } // 設置監聽,主要是監聽popstate方法來自動觸發transitionTo setupListeners () { if (this.listeners.length > 0) { return } const router = this.router const expectScroll = router.options.scrollBehavior const supportsScroll = supportsPushState && expectScroll // 若支持scroll,初始化scroll相關邏輯 if (supportsScroll) { this.listeners.push(setupScroll()) } const handleRoutingEvent = () => { const current = this.current // 某些瀏覽器,會在打開頁面時觸發一次popstate // 此時如果初始路由是異步路由,就會出現`popstate`先觸發,初始路由后解析完成,進而導致route未更新 // 所以需要避免 const location = getLocation(this.base) if (this.current === START && location === this._startLocation) { return } // 路由地址發生變化,則跳轉,如需滾動則在跳轉后處理滾動 this.transitionTo(location, route => { if (supportsScroll) { handleScroll(router, route, current, true) } }) } // 監聽popstate事件 window.addEventListener('popstate', handleRoutingEvent) this.listeners.push(() => { window.removeEventListener('popstate', handleRoutingEvent) }) } // 可以看到 history模式go方法其實是調用的window.history.go(n) go (n: number) { window.history.go(n) } // push方法會主動調用transitionTo進行跳轉 push (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) { const { current: fromRoute } = this this.transitionTo(location, route => { pushState(cleanPath(this.base + route.fullPath)) handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false) onComplete && onComplete(route) }, onAbort) } // replace方法會主動調用transitionTo進行跳轉 replace (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) { const { current: fromRoute } = this this.transitionTo(location, route => { replaceState(cleanPath(this.base + route.fullPath)) handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false) onComplete && onComplete(route) }, onAbort) } ensureURL (push?: boolean) { if (getLocation(this.base) !== this.current.fullPath) { const current = cleanPath(this.base + this.current.fullPath) push ? pushState(current) : replaceState(current) } } getCurrentLocation (): string { return getLocation(this.base) } } export function getLocation (base: string): string { let path = window.location.pathname const pathLowerCase = path.toLowerCase() const baseLowerCase = base.toLowerCase() // base="/a" shouldn't turn path="/app" into "/a/pp" // https://github.com/vuejs/vue-router/issues/3555 // so we ensure the trailing slash in the base if (base && ((pathLowerCase === baseLowerCase) || (pathLowerCase.indexOf(cleanPath(baseLowerCase + '/')) === 0))) { path = path.slice(base.length) } return (path || '/') + window.location.search + window.location.hash }
可以看到HTML5History類主要干了如下幾件事。
-
繼承于
History類,并調用父類構造函數初始化。 -
實現了
setupListeners方法,在該方法中檢查了是否需要支持滾動行為,如果支持,則初始化滾動相關邏輯,監聽了popstate事件,并在popstate觸發時自動調用transitionTo方法。 -
實現了
go、push、replace等方法,我們可以看到,history模式其實就是使用的history api。
// 可以看到 history模式go方法其實是調用的window.history.go(n) go (n: number) { window.history.go(n) } // push、replace調用的是util/push-state.js,里面實現了push和replace方法 // 實現原理也是使用的history api,并且在不支持history api的情況下使用location api export function pushState (url?: string, replace?: boolean) { ... const history = window.history try { if (replace) { const stateCopy = extend({}, history.state) stateCopy.key = getStateKey() // 調用的 history.replaceState history.replaceState(stateCopy, '', url) } else { // 調用的 history.pushState history.pushState({ key: setStateKey(genStateKey()) }, '', url) } } catch (e) { window.location[replace ? 'replace' : 'assign'](url) } } export function replaceState (url?: string) { pushState(url, true) }
總結
所以history模式的原理就是在js中路由的跳轉(也就是使用push和replace方法)都是通過history api,history.pushState 和 history.replaceState兩個方法完成,通過這兩個方法我們知道了路由的變化,然后根據路由映射關系來實現頁面內容的更新。
對于直接點擊瀏覽器的前進后退按鈕或者js調用 this.$router.go()、this.$router.forward()、this.$router.back()、或者原生js方法history.back() 、history.go()、history.forward()的,都會觸發popstate事件,通過監聽這個事件我們就可以知道路由發生了哪些變化然后來實現更新頁面內容。
注意history.pushState 和 history.replaceState這兩個方法并不會觸發popstate事件。在這兩個方法里面他是有手動調用transitionTo方法的。
接下來我們再來看看HashHistory類
HashHistory類
當我們使用hash模式的時候會實例化HashHistory類。
//src/history/hash.js ... export class HashHistory extends History { constructor (router: Router, base: ?string, fallback: boolean) { super(router, base) // check history fallback deeplinking if (fallback && checkFallback(this.base)) { return } ensureSlash() } setupListeners () { if (this.listeners.length > 0) { return } const router = this.router const expectScroll = router.options.scrollBehavior const supportsScroll = supportsPushState && expectScroll if (supportsScroll) { this.listeners.push(setupScroll()) } const handleRoutingEvent = () => { const current = this.current if (!ensureSlash()) { return } this.transitionTo(getHash(), route => { if (supportsScroll) { handleScroll(this.router, route, current, true) } if (!supportsPushState) { replaceHash(route.fullPath) } }) } // 事件優先使用 popstate // 判斷supportsPushState就是通過return window.history && typeof window.history.pushState === 'function' const eventType = supportsPushState ? 'popstate' : 'hashchange' window.addEventListener( eventType, handleRoutingEvent ) this.listeners.push(() => { window.removeEventListener(eventType, handleRoutingEvent) }) } // 其實也是優先使用history的pushState方法來實現,不支持再使用location修改hash值 push (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) { const { current: fromRoute } = this this.transitionTo( location, route => { pushHash(route.fullPath) handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false) onComplete && onComplete(route) }, onAbort ) } // 其實也是優先使用history的replaceState方法來實現,不支持再使用location修改replace方法 replace (location: RawLocation, onComplete?: Function, onAbort?: Function) { const { current: fromRoute } = this this.transitionTo( location, route => { replaceHash(route.fullPath) handleScroll(this.router, route, fromRoute, false) onComplete && onComplete(route) }, onAbort ) } // 也是使用的history go方法 go (n: number) { window.history.go(n) } ensureURL (push?: boolean) { const current = this.current.fullPath if (getHash() !== current) { push ? pushHash(current) : replaceHash(current) } } getCurrentLocation () { return getHash() } } function checkFallback (base) { const location = getLocation(base) if (!/^/#/.test(location)) { window.location.replace(cleanPath(base + '/#' + location)) return true } } function ensureSlash (): boolean { const path = getHash() if (path.charAt(0) === '/') { return true } replaceHash('/' + path) return false } // 獲取 # 后面的內容 export function getHash (): string { // We can't use window.location.hash here because it's not // consistent across browsers - Firefox will pre-decode it! let href = window.location.href const index = href.indexOf('#') // empty path if (index < 0) return '' href = href.slice(index + 1) return href } function getUrl (path) { const href = window.location.href const i = href.indexOf('#') const base = i >= 0 ? href.slice(0, i) : href return `${base}#${path}` } function pushHash (path) { if (supportsPushState) { pushState(getUrl(path)) } else { window.location.hash = path } } function replaceHash (path) { if (supportsPushState) { replaceState(getUrl(path)) } else { window.location.replace(getUrl(path)) } }
可以看到HashHistory類主要干了如下幾件事。
-
繼承于
History類,并調用父類構造函數初始化。這里比HTML5History多了回退操作,所以,需要將history模式的url替換成hash模式,即添加上#,這個邏輯是由checkFallback實現的 -
實現了
setupListeners方法,在該方法中檢查了是否需要支持滾動行為,如果支持,則初始化滾動相關邏輯。 監聽了popstate事件或hashchange事件,并在相應事件觸發時,調用transitionTo方法實現跳轉。
通過
const eventType = supportsPushState ? 'popstate' : 'hashchange'我們可以發現就算是hash模式優先使用的還是popstate事件。
-
實現了
go、push、replace等方法。
我們可以看到,hash模式實現的push、replace方法其實也是優先使用history里面的方法,也就是history api。
// 可以看到 hash 模式go方法其實是調用的window.history.go(n) go (n: number) { window.history.go(n) } // 在支持新的history api情況下優先使用history.pushState實現 // 否則使用location api function pushHash (path) { if (supportsPushState) { pushState(getUrl(path)) } else { window.location.hash = path } } // 在支持新的history api情況下優先使用history.replaceState實現 // 否則使用location api function replaceHash (path) { if (supportsPushState) { replaceState(getUrl(path)) } else { window.location.replace(getUrl(path)) } }
總結
在瀏覽器鏈接里面我們改變hash值是不會重新向后臺發送請求的,也就不會刷新頁面。并且每次 hash 值的變化,還會觸發hashchange 這個事件。
所以hash模式的原理就是通過監聽hashchange事件,通過這個事件我們就可以知道 hash 值發生了哪些變化然后根據路由映射關系來實現頁面內容的更新。(這里hash值的變化不管是通過js修改的還是直接點擊瀏覽器的前進后退按鈕都會觸發hashchange事件)
對于hash模式,如果是在瀏覽器支持history api情況下,hash模式的實現其實是和history模式一樣的。只有在不支持history api情況下才會監聽hashchange事件。這個我們可以在源碼中看出來。
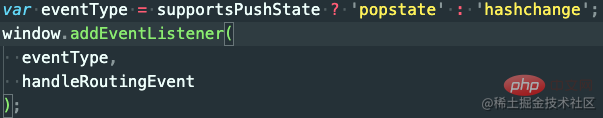
總結
總的來說就是使用 Vue.util.defineReactive 將實例的 _route 設置為響應式對象。在push, replace方法里會主動更新屬性 _route。而 go,back,forward,或者通過點擊瀏覽器前進后退的按鈕則會在 hashchange 或者 popstate 的回調中更新 _route。_route 的更新會觸發 RoterView 的重新渲染。
對于第一次進入系統,并不會觸發hashchange或者popstate事件,所以第一次需要自己手動匹配路徑然后通過transitionTo方法進行跳轉,然后渲染對應的視圖。
(學習視頻分享:web前端開發、編程基礎視頻)
 站長資訊網
站長資訊網